Feature
Huge amounts of single-use masks and gloves are already being found in the sea damaging marine life
Some bad news for the environment…
Published
4 years agoon
By
Alex Watson
The rise in disposable face masks, plastic gloves and bottles of hand sanitiser being used to prevent the spread of coronavirus are adding massively to plastic pollution and threatening the health of oceans and marine life.
Across social media, many members of the public have shared pictures of the bright blue gloves and crumbled masks littering streets and parking lots after being discarded around the world.
In most situations, this litter is left to frontline workers to clean up. Those not picked up can be washed down drains and end in waterways and oceans.
In Los Angeles, city officials have boosted fines regarding littering due to the danger dropping contaminated products may pose towards others.
While no-one can dispute the current urgency and importance of PPE, many of these single-use products have already ended up in the oceans, damaging the ecosystem and contributing to plastic pollution.
This influx of surgical masks on our beaches following the social change resulting from the #coronavirus indicates that we have a serious problems with #WasteManagement systems in #HongKong & #China.
— OceansAsia (@oceansasia1) March 1, 2020
*Gloves were worn at all times + all collected masks were disposed of properly. pic.twitter.com/WOq8Klbylc
The WWF has reported that if as little as 1% of masks were disposed of incorrectly and dispersed in nature, this would mean 10 million masks a month polluting the environment.
The report also states that despite each mask weighing as little as 4 grams, it would result in 40,000kg of plastic in nature.
Dropping PPE in this sense is not only a hazardous health risk, but most of the equipment is single-use materials that can’t be recycled and/or are not biodegradable.
Surgical masks, for instance, are made of non-woven fabrics that include plastics like polypropylene.
Many nature projects such as Operation Mer Propre in France has filmed masks and gloves found at the bottom of the waters of the Mediterranean.

It is widely known the disastrous effects plastic has on marine ecosystems. The National Ocean Service explains that plastic doesn’t decompose and instead breaks into tiny pieces called microplastics.
The Ocean Conservancy discovered that fish species consume plastic debris, confusing it for real food.
The brightly coloured latex gloves are being mistaken by seabirds, turtles and other marine mammals as food putting them at risk of severe injuries and death.
An early warning sign of the effects of single-use PPE came back in February when OceansAsia posted a photo with dozens of surgical masks found on Hong Kong beaches.

Plastic has regularly been found in dead marine wildlife, and in 2019 a sperm whale stranded on the Isle of Harris in Scotland was found to have 220lb of debris in its stomach including rope, plastic gloves, bags and cups.
Co-founder of OceansAsia, Gary Stokes, told The Independent: “I’m waiting to hear of the first necropsy that finds masks inside a dead marine animal. It’s not a question of if, but when.”
The Policy Director on Chemicals and Pollution at Greenpeace, Kevin Stairs, has said that there is no scientific evidence that single-use plastics are better than reusable ones.
He said: “When reusing a PPE, we disinfect it. With single-use products, the item is fugitive, escapes the system and can carry the Sars-CoV-2 virus for days on its surface.”
A professor in marine biology at the University of Plymouth, Richard Thompson, has said that while we should not ‘delay giving everyone PPE’ due to the ‘crisis and immense pressure’ we are currently facing, people need to be told how to dispose of them correctly.
He also said that sustainability practices backtrack in a crisis, explaining that the sea is not littered by the use of the product but the way in which it is disposed of.
As such, if the design of any product was made in a way that is easier to recycle and reuse there could be less waste from such products, ‘whether it’s a bottle of lemonade or a mask that’s used in a hospital’.
Over 370,000 people have died from coronavirus worldwide and it is imperative we continue to practice safe methods such as social distancing, but there are increasingly more and more sustainable options to single-use products, even in the pandemic.
#MarinePlastic #PlasticPollution wreaks havoc on marine ecosystems and kills wildlife.
— OceansAsia (@oceansasia1) April 26, 2020
We found these masks after only 5 minutes on a #HongKong beach.@MingPaoCom @HongKongFP@thestandardHk @hongkong_news@singtaodaily @asiatimesonline@appledaily_hk pic.twitter.com/L0JTGznKU4
The World Health Organisation has said that washing hands regularly is more effective than wearing gloves at preventing the spread of the virus.
There are also sustainable innovations slowly beginning to emerge, such as the use of ultraviolet light in decontaminating, and therefore prolonging the life of medical masks.
COVID-19 also remains on plastic longer than almost any material examined (in laboratory conditions) so opting for plastic covered food isn’t necessarily the better option.
The European Food Safety Authority has also said: “There is currently no evidence that food is a likely source or route of transmission of COVID-19”, and that heat during cooking kills the virus.
To cut back on laundry during the pandemic, individuals can consider an ‘outside set of clothes’ that can be removed immediately and stored in a closed bag, giving the virus time to die off.
To limit the number of times you visit the shop and reduce your overall carbon footprint you could opt for a vegetarian or vegan diet, including growing your own vegetables in gardens or balconies and in some cases window ledges or received veg deliveries from local farmers.
You may like
-


United Utilities announces it’s ending grouse shooting on its moorlands
-


Chris Martin spotted catching train from Manchester to Cardiff
-


BrewDog’s plan to add ‘bug burger’ to its menu divides internet
-


Sainsbury’s defends new vacuum-packed minced beef that ‘turns to mush’
-


Plastic wet wipes set to be banned across England
-


Manchester’s ‘first public city centre park’ to open this week
Feature
Memories of demolished Trafford Park Bakery from the people that worked there
From bomb threats, to falling asleep on conveyor belts, to eating space cakes – fun times and sad times happened here, until one day it was all over
Published
3 months agoon
April 19, 2024
Trafford Park was once home to a huge bakery where workers would ‘get up to no good’ but still ‘get the job done’, until one day it closed for good. Here’s their tales from the Trafford Park Bakery days.
It once stood on Ashburton Road West in the industrial maze that is Trafford Park, until it was torn down in 2008.
The bakery was known for offering well paid jobs to people living in the surrounding areas, attracting workers from Eccles, Urmston, Stretford, Salford and Stockport, as well as a number of agency staff.
When the recession happened in the 1980s, a lot of tradespeople found themselves out of work, and for a steady income many of them took up employment at Trafford Park Bakery.

Ex-United defender Bobby Noble also got a job there. He had to retire early from football at the age of 23 after he was injured in a road accident, which damaged his sight and the ability to judge the flight of the ball.
He played among the likes of Best, Law, Stiles and Charlton and helped the team achieve League title victory in the 1966/67 season. Sadly, Bobby passed away last year, but his former colleagues remember him as ‘a lovely man’ and ‘funny guy’ with ‘great stories’.
Employees enjoyed the times they had at the bakery with their mates so much, they even set up a Facebook group after it closed down called ‘Trafford Park Bakery…They think it’s all over! It is now….’ to stay in touch and remember the best times.
Clare Callaghan got a job there after previously doing part-time work to fit around her children.

About how she came to work at the bakery, Clare says: “I’d never had a job like that before, I always worked in pubs, cleaning and doing school dinners – whatever fitted in with the kids.”
But when Clare’s kids got a bit older and went to school, she looked for full-time work and landed a job at the bakery as a quiche assembler.
She remembers: “I’ll never forget walking along the high corridor with glass windows on each side so you could see the production areas. And then you walked over to the assembly area where they actually made the stuff and all the machines were on and I thought ‘oh my god’, you know, it looked like Willy Wonka’s.”

Describing her job, she said: “So there was a conveyor belt and four girls on scales putting peppers and goats cheese on the quiches and then I topped them off with parmesan cheese. So I was just stood there sprinkling parmesan all shift. Sometimes my eyes would be closing.”
About the people she worked with, Clare said: “Every line was fun but our line was good fun. It was a mixture of younger and older women and men.”
Clare was quickly made the new line leader ‘in no time’ after one person got sacked and another moved to nights after photos of them ‘misbehaving’ at work fell into the hands of senior management.
Mike Minshall trained Clare up to work in the quiche department when she first started.

On how he found a job at the bakery, Mike said: “I actually found out through one of the national papers – my wife told me.
“And I applied and one of the daft questions was: ‘If we made nuts and bolts and we did 10 an hour, how many would we do in eight hours?’ In my answer, I put: ‘I thought you made pies?’
“The girl interviewing me was called Janet and she went: ‘Right, you’re in because you’re the only one who’s given me a daft answer’.”
Mike recalled his first day on shift, saying: “On my first day at work, I met my boss Pete – who I thought the world of. I went, ‘what do I have to do?’, he went, ‘lean against that wall’. I went, ‘what?’. He went, ‘lean against that wall and every time he [one of his colleagues] walks past, say knobhead.’”

“So I asked why and he told me that the guy was asked to clean the machine and he put a hose pipe in the panel and blew it up.
“He told me that was my job for the day; to lean against the wall and call him a knobhead.”
Remembering other hilarious happenings, Mike said: “My friend fell asleep on a conveyor belt and he was lucky he didn’t get dropped into the pastry cutter. He was on the hygiene team.
“One time, I walked into my department and this gentleman is there on his back in a machine that we wash the trays in, having a cigarette because it had an extractor fan. He’s lucky it was me.”

“There’s all sorts of different stories, there were affairs going on – there were 800 people who worked there,” he continued.
As Mike also recalled: “Our taps were touch sensitive so if you brushed past the tap it came on. So, this gentleman was telling someone who couldn’t work the water, ‘you have to be more assertive and say, water, as you brush past the sensor’.
“So this lad kept saying ‘water’ and getting told it’s not working because he needs to be more assertive when he says it.
“After 20 minutes this was guy was shouting ‘I want water, give me the effing water!’ When all he had to do was brush it.”

R worked at the bakery from 1988 on the Hygiene Department doing night shifts. He was also a line leader.
Remembering one funny incident, he said: “I remember one day the boss walked in while we were in the middle of working and told us that an animal rights organisation had been on the phone and issued a bomb threat to the bakery.
“So we were like ‘right’ and started to put everything down and make our way out of the door. But the boss was like ‘no, not yet, it’s not until 1 ‘o’ clock, carry on with what you’re doing’.
“We were all just laughing at him and was like, ‘I don’t think so’ and carried on walking out.”

Another time, R recalled a new lad staring on his line who was a ‘hard worker’ and so he mentioned to his boss to help make him feel welcomed so they could keep him working on their line.
He offered the new lad a lift into work if he was ever stuck for getting in. A number of weeks went by until one particular morning, the lad did call R before work and asked if he could pick him up on route.
He told him his girlfriend’s ex-boyfriend had spotted him and was chasing him around the streets and so he was hiding in some bushes.
“I said ‘no problem, mate’ not thinking anything of it,” R said.

R pulled up and the new lad jumped in and was keeping his head down. R continued: “I told him ‘there’s no need to worry now, you’re in the car. But as we were driving in the car lit up and I was like ‘why’s the car lighting up? Is that a helicopter?’.
“Anyway, we got to work and I didn’t think anything of it. But later on my manager pulled me and told me I had to tell the new lad he was needed at the nurses’s station.
“They told me not to tell anyone and to keep it to myself. Straight away I knew what they meant and so I told him to go to the nurses station and police came to take him away in handcuffs.
“He was a really nice lad and a good worker, but it turns out he was a car thief too.”

Clare remembers another time when someone brought in ‘space cakes’ on a night shift and that one of the guys on the line ate one ‘and his head nearly fell off,’ she laughed.
The fun times kept on coming as people made friends for life at Trafford Park Bakery, until one day, news broke it was closing down and those good times would become fond memories etched in the minds of those who once worked there.
On his time at Trafford Park Bakery, Mike said: “I loved every minute of it there and if it was still there, I’d still be there. I worked there for 10 years before it shut. When it was closing down, I was told before everyone else. But it was announced on the BBC before they told everyone.
“My late wife rang me and told me ‘you’ve all lost your jobs’, and we were told to not talk to the media or you could jeopardise your redundancy. I miss my team. People move on but I do miss people. I miss the Christmas dinners there because the senior management had to serve you, and I’d be bossing them around.”

After the bakery closed, Mike went to work for Peugeot but didn’t like it. He then went back to ‘what I was good at’, which was repairing wagons. But he said he ‘didn’t like getting full of oil’. He then went to work for Rivita and West Mill at Trafford Park but is retired now.
He added: “I’ve had an interesting time but the best time was when I was there [at Trafford Park Bakery] with that lot because they were all crackers.”
About her time working there, Clare added: “It was ace. I mean, we got the work done, and everyone used to moan about the place but it didn’t matter what shift you were on, you knew everyone – it was just brilliant, you could make a television series out of it.
“But I mean, some of the things I couldn’t repeat!”
Clare still keeps in touch with Barbara who worked on her line and goes to visit her sometimes for a catch up.
Feature
Remembering Manchester’s lost underground market that now lies empty beneath the city
Do you have memories of shopping in the underground Market Centre?
Published
4 months agoon
March 14, 2024
Manchester used to have an underground market that now lies abandoned beneath the city centre.
If you walk along Market Street, you’re walking above what used to be the Market Centre – an underground shopping area filled with stalls and units selling music, clothes and a variety of other essential and non-essential items.
The underground Market Centre opened in 1972 and was a busy and bustling shopping emporium, much like the Arndale and Market Street both are today.

Punks would shop there for outfits, music fans could browse through the vinyl record shops and buy tickets to gigs at Piccadilly Box Office. It even had a Stolen from Ivor – which was the first place in Manchester to sell the jeans brand Levi’s, and where many would flock to get their hands on a pair of 501s.
Fashion addicts could hit up shops including Roxy, Oasis and Justins as well as a number of other boutique stalls, including the leather shop, for cool jackets.
DJs could sift through the collections at Underground Records Import and fans could shop at iconic music stalls including Collectors Records, Yvonne’s Record Stall, and the Spinn Inn Disc Centre.


The Market Centre was the place to be throughout the ‘70s and ‘80s until it closed down in 1989.
The entrance to it was located on Brown Street, with two other entrances on Norfolk Street and Spring Gardens. It had escalators going down under the pavement that led to this total treasure trove.
If you head to the Tesco on Market Street and go down to the lower level, you’re actually in what used to be part of the underground market.
But now it has fallen into disrepair, with the odd urban explorer who has dared to delve into the depth of the city to see what remains of this now eerie, decaying ghost market.
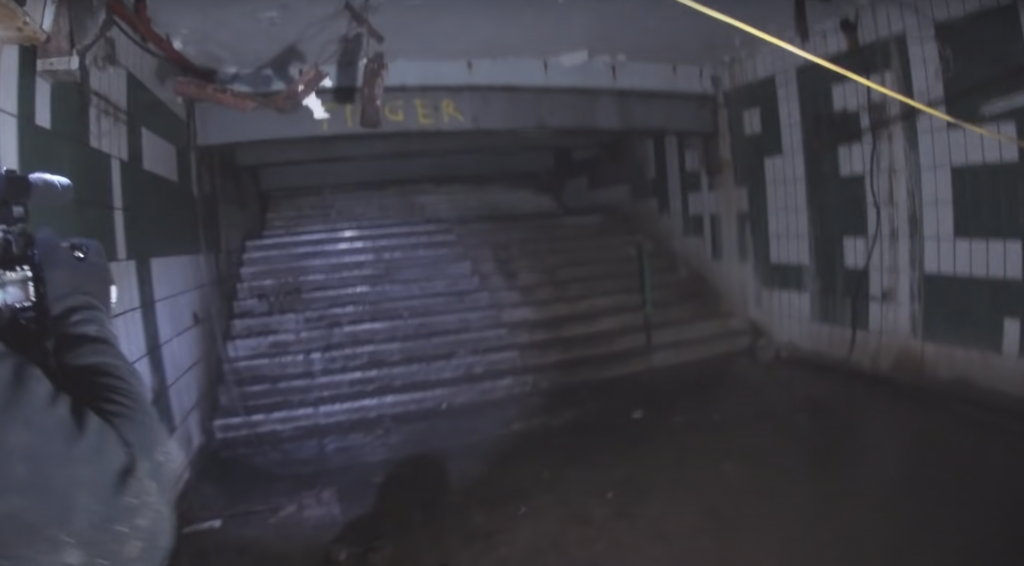


One explorer, known as Urban Sherman on YouTube, went down to have a look at what’s left of these once bustling underground stalls. Finding a way into where the old main entrance was located, down by the side of Tesco behind the food trailer, he climbs in and lands on the old steps with tiled walls.
As torches light up the dark depths of the city, we can see wires hanging, rubble strewn across the floor, graffiti on walls and one rusty sign that reads: “factory prices.”
It appears a wall of breeze blocks has been put up to block off any entry along the halls of the former market with the rest of it inaccessible, only to live on in the memories of those who once shopped there, and in old archived photographs.
Got a story to tell?
Have you got a story or video you think our audience will love? We want to hear from you, drop us an email on submit@propermanchester.com and we’ll get back to you.
Feature
The legendary nightclubs that Mancunians would most like to bring back
Remember any of these?
Published
5 months agoon
March 8, 2024
We asked our readers which nightclubs that no longer exist they would choose to bring back – and we got some great answers.
If you could choose just one, which would it be?
Here’s a list of former nightclubs that people would love to see return, as chosen by Proper Manchester readers.

The Boardwalk
The Boardwalk was a nightclub based on Little Peter Street in Manchester which was open from 1986 to 1999. It was a multi-floor nightclub, gig venue and rehearsal complex all in one.
It’s where Oasis played their first ever gig in 1992 and saw many notable bands that were a part of the Madchester music scene, including the likes of Inspiral Carpets, Doves, Happy Mondays, James and more. These days, it’s used as an office space.
There’s a blue plaque bolted to the wall which reads: “Remember me. I was something once.” It has a yellow smiley face in a nod to the Madchester acid house era.

Club Phoenix
Located on University Precinct, on Oxford Road, this sweatbox of a student dive would have music blaring on different nights, playing everything from indie bangers to dance classics and everything in between.
It was a scream club filled with young students looking for cheap drinks and cheap thrills too. There were plenty of messy drunken shenanigans. Being close to the Academy, it would be a great place for the young ‘uns to go for pre-gig bevvies.

The New Continental Club
The New Continental Club was on Harter Street, Manchester and opened in 1967. It was affectionately known as The Conti. It closed in 2001 and became The Tube nightclub, which has also since closed.
Many nurses and frontline emergency services workers frequented The Conti and many say they experienced some of the best nights out of their lives.
The narrow staircase would lead down to the basement club, food would be served through a hatch and the queues to the toilets could be as long as your arm – they were pretty minging too.

Discotheque Royales
Built in 1845, the building was originally made to be an amphitheatre. But in 1921 it was changed into a cinema after facing stiff competition from the Palace Theatre and Opera House.
After being used as a bingo hall, the historic landmark then became one of Manchester’s most iconic nightclubs known by most as ‘Royales’, since 1989. In later years it went on to become Infinity and M-Two but Royales was legendary throughout the ‘90s.
Inside, it had many levels and a huge dance floor that was meant to look like it was lit up under a huge chandelier. With long draped velvet curtains, lights and reflective mirrors everywhere, it was party central.
DJ Brutus Gold held Love Train nights there until the show moved to the Ritz in 2000.

Fifth Avenue
This club started out as Legend, which became known as Manchester’s ‘other club’ during the ‘80s and the height of the Hacienda era, and saw top DJs who also played nights at Wigan Pier.
When it became Fifth Ave it was transformed into an indie music haven. As revellers walked down into the dingy basement and the whiff of cheap bleach in the air would hit them in the face, some of the best tunes from Manchester bands would be blasting, as partygoers walked straight across the sticky floor to the bar where they’d order a drink served in a plastic cup.
Club-goers soon got to know that if you went up to request a song from the DJ, it wouldn’t get played. In later years, it became known simply as Fifth, after owners tried a bit of a refresh.
But as the pandemic hit, the club sat empty and shuttered, and sadly never to return as it closed for good in 2021.

Twisted Wheel Club
It quickly became a Manchester institution after opening in the ‘60s, attracting mods across the North looking for somewhere to dance all night to rhythm and blues.
Before Twisted Wheel, clubs would play mainstream popular music. This Manchester establishment was groundbreaking and paved the way for how nightclubs would play different music genres to suit various tastes in the future.
Twisted Wheel, based on Swan Street, was a legendary haven for Northern Soul enthusiasts. It closed for a while in 1971, being renamed Placemate 7, then Follies. The club closed for good in 2021.

Thunderdome
If the Hacienda was too pretentious for you, or you got turned away at the door, there was another legendary Madchester club playing all the great acid house music buzzing dancers wanted to rave the night away to – it was called the Thunderdome.
Located at 255 Oldham Road, this club was all about the music. It was edgier, full of all walks of life and was even home to some of Manchester’s criminal underworld. Many fondly referred to it as the ‘Dome.
Initially, although it felt a bit dangerous, nobody wanted any trouble, they just wanted to get off their trolley and enjoy the music. But over the years there were police raids and even helicopters circling the club as well as undercover officers wearing yellow smiley face T-shirts mingling in amongst the hooligans, gang members and just generally dodgy people.
Unfortunately, its rough reputation has stuck with it to this day, while the Hacienda is remembered most as the epicentre of the Madchester acid house scene. The Thunderdome was demolished in 2010 but its legend lives on in the memories of retired ravers and on tribute Facebook groups.
Find something to do in Manchester

Huge beer festival with more than 500 different varieties coming to Manchester

New makers market with everything from dog accessories to house plants and jewellery coming to Manchester

New apartment development with huge gardens and outdoor space opening this year

Stagecoach hiring over 100 new bus drivers for Bee Network with £31k salaries

Manchester Flower Festival returns with tributes to Sarah Harding and Caroline Aherne